How do you explain numerator and denominator to a child?
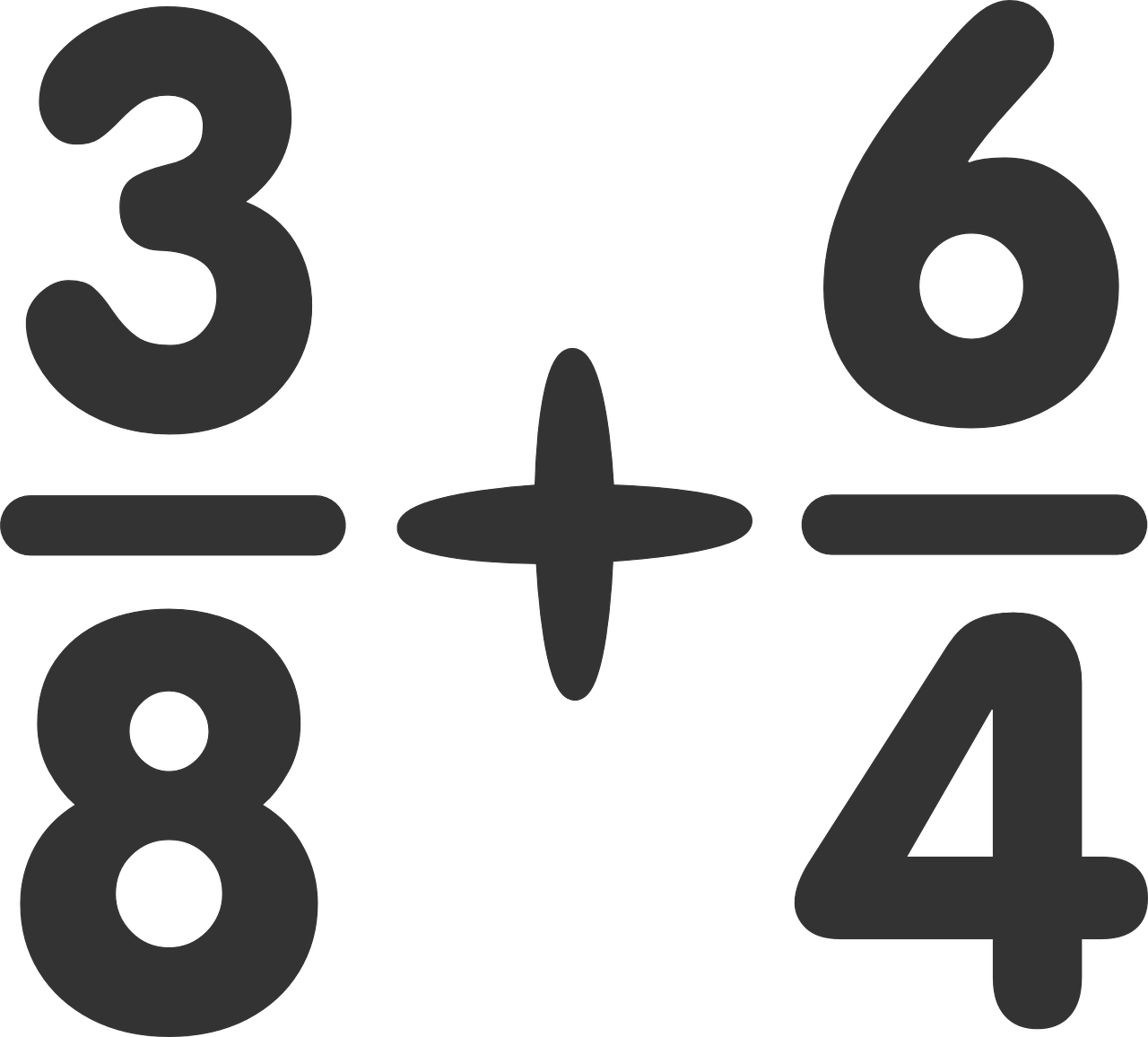
The numerator and denominator are important concepts in mathematics that help us understand fractions. When we talk about fractions, we are referring to a part of a whole. The numerator represents the number of parts we have, while the denominator represents the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
For example, let's imagine we have a pizza. The pizza is divided into 8 equal slices. If we want to talk about how many slices we have, we would use the numerator. If we have eaten 3 slices of the pizza, then the numerator would be 3. The denominator would still be 8, because the pizza is still divided into 8 slices in total.
So, the fraction 3/8 means we have eaten 3 out of the 8 total slices of pizza. The numerator tells us how many slices we have, and the denominator tells us the total number of slices the pizza is divided into.
In addition, we can use the numerator and denominator to compare fractions. If we have another pizza that is divided into 4 slices, and we have eaten 2 slices, then the fraction would be 2/4. We can simplify this fraction by dividing both the numerator and denominator by 2. As a result, we get 1/2. So, 2/4 is equivalent to 1/2.
Understanding the numerator and denominator is crucial for working with fractions in math. By knowing how to interpret and manipulate these numbers, we can perform operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with fractions.
So, next time you see a fraction, remember that the numerator represents the number of parts you have, and the denominator represents the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
How do you explain numerator and denominator for kids?
Understanding fractions can be a challenging task for children, but explaining the concept of numerator and denominator in a simple way can make it easier for them to grasp.
Firstly, it is important to explain that fractions are numbers that represent parts of a whole. The numerator is the number on top of the fraction and it tells us how many parts we have. For example, in the fraction 3/5, the numerator is 3, which means we have 3 parts of the whole.
Next, we introduce the denominator. The denominator is the number at the bottom of the fraction and it tells us how many equal parts the whole is divided into. Using the same example of 3/5, the denominator is 5, which means the whole is divided into 5 equal parts.
Now, we combine the numerator and denominator to understand the fraction as a whole. We can explain to the children that when we say the fraction 3/5, we are saying that we have 3 out of the 5 equal parts of the whole.
Furthermore, it is essential to provide visual aids to help children visualize the concept of numerator and denominator. Using shapes or pictures divided into equal parts can make it easier for them to understand how the parts relate to each other.
In conclusion, explaining the numerator and denominator to children involves introducing the concepts of parts of a whole, the number of parts we have (numerator), and the number of equal parts in the whole (denominator). Visual aids can greatly enhance their understanding. Remember to keep the explanations simple and interactive to make it more engaging for the kids.
How is a denominator defined for kids?
In mathematics, the denominator is an essential component when dealing with fractions. For kids, understanding the concept of a denominator can sometimes be challenging.
Denominator refers to the bottom number in a fraction. It represents the total number of equal parts into which a whole is divided. To put it simply, the denominator tells us the total number of parts that make up a whole.
For example, let's consider the fraction 3/4. Here, the denominator is 4, indicating that the whole is divided into four equal parts. Each part represents 1/4 of the whole.
Understanding the denominator is crucial when comparing and operating with fractions. When adding or subtracting fractions, the denominators must be the same. If they are different, the fractions need to be converted to have a common denominator before performing the operation.
Additionally, the denominator also helps us determine the size or value of a fraction. The higher the value of the denominator, the smaller each part will be, resulting in a smaller fraction. Conversely, a lower denominator indicates larger parts, resulting in a larger fraction.
It is important to introduce the concept of denominators gradually to kids, using visual aids such as diagrams or manipulatives. This helps them visualize how a whole can be divided into equal parts and understand the role of the denominator in representing those parts.
By providing clear explanations and offering plenty of practice opportunities, kids can develop a solid understanding of denominators and confidently work with fractions in their math journey.
What is the numerator and denominator in ks1?
What is the numerator and denominator in ks1?
The numerator and denominator are mathematical terms used to represent fractions. In KS1, which stands for Key Stage 1, these terms are introduced to students as part of their foundational math education.
The numerator refers to the top number in a fraction. It represents the number of parts we are considering or counting. For example, in the fraction 3/5, the numerator is 3. It tells us that we are considering or counting 3 parts out of a total of 5.
The denominator is the bottom number in a fraction. It represents the total number of parts that make up a whole. In the fraction 3/5, the denominator is 5. It tells us that the whole is divided into 5 equal parts.
Understanding the numerator and denominator is crucial in learning how to compare and operate with fractions. Students in KS1 begin by working with simple fractions, such as halves, thirds, and quarters. They learn to recognize and write fractions using both numerical and visual representations.
As students progress through KS1, they are introduced to more complex fractions and learn how to convert between different representations, such as fractions and decimals.
Overall, the numerator and denominator are fundamental concepts in fractions, and having a solid understanding of these terms lays the groundwork for future math learning in KS1 and beyond.
How do you explain fractions to a child?
Explaining fractions to a child can sometimes be challenging, but with the right approach and examples, it can become an enjoyable learning experience. Fractions are a fundamental concept in mathematics, and it is essential to explain them in a way that is easy for children to understand.
One way to explain fractions is by using visual aids such as pictures or objects. For example, you can use a pizza cut into slices to represent fractions. Explain to the child that fractions represent a part of a whole. Each slice of pizza represents a fraction. If the pizza is divided into eight slices, one slice would be written as 1/8. This visual representation helps the child grasp the concept of fractions.
Another approach to explaining fractions is by using real-life examples. For instance, when baking cookies, you can explain that if you have 8 cookies and you want to share them equally among 4 friends, each person would get 2 cookies. This can be written as 2/8. By relating fractions to familiar situations, children can better understand the concept.
Additionally, it is crucial to emphasize the relationship between fractions and numbers. For example, explain that a fraction such as 1/2 is the same as saying "one out of two." Encourage children to think of fractions as a division problem, where the numerator represents the number being divided and the denominator represents the number of equal parts the whole is divided into.
In conclusion, explaining fractions to a child can be done effectively through the use of visual aids, real-life examples, and emphasizing the relationship between fractions and numbers. By engaging children in hands-on activities and providing relatable examples, they can develop a solid understanding of fractions.
