What are the 4 steps to using a Venn diagram?
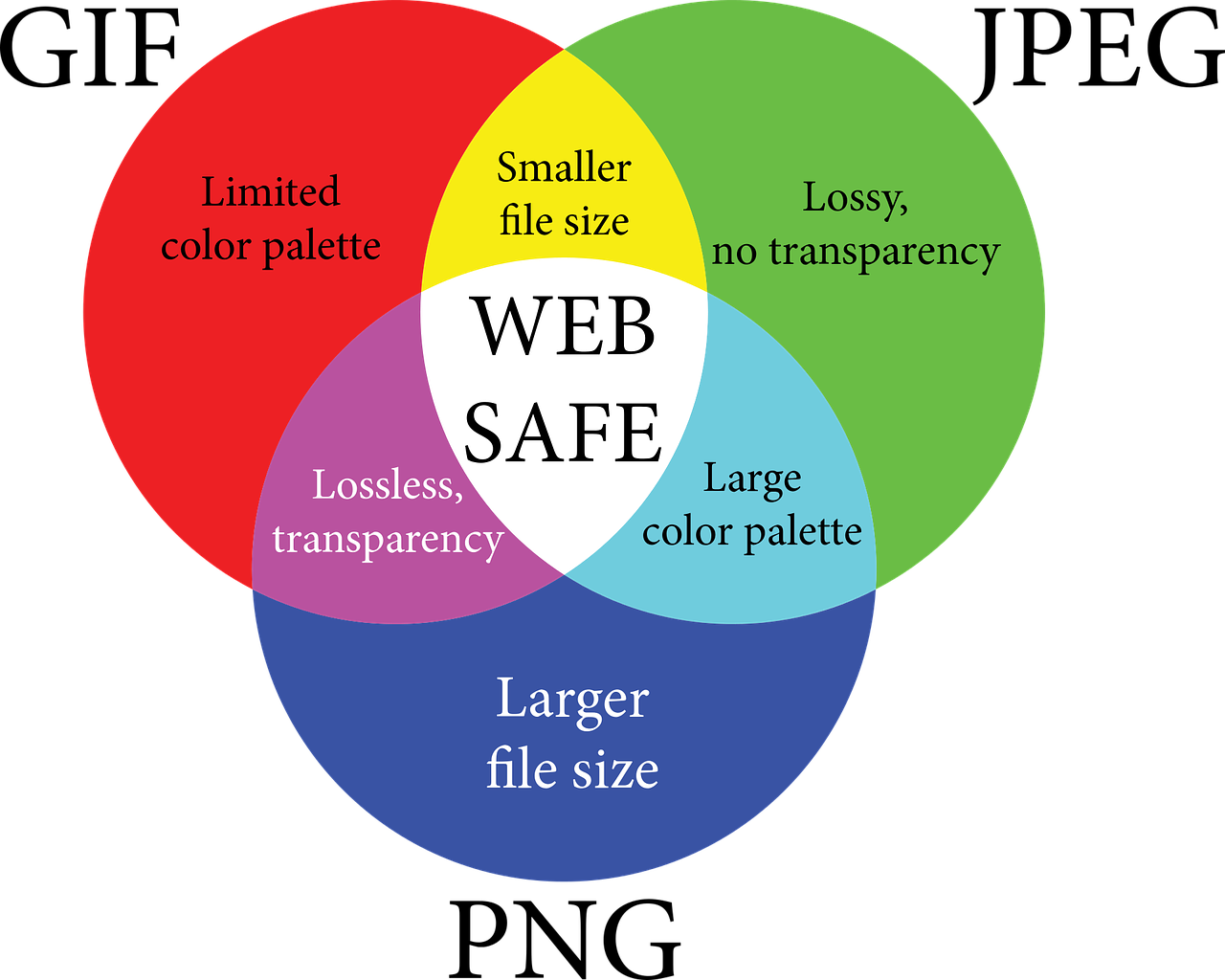
Venn diagrams are useful tools for visualizing relationships between different sets of data. Here are the four steps to using a Venn diagram effectively:
Step 1: Identify the sets to be compared
Begin by determining the different sets or groups you want to compare using the Venn diagram. For example, if you want to compare the characteristics of dogs and cats, the two sets would be "dogs" and "cats".
Step 2: Draw overlapping circles
Next, draw circles for each set, with their corresponding labels. These circles should overlap in the center to show the common elements between the sets. In our example, one circle would represent "dogs" and the other would represent "cats", with the overlapping area representing common traits shared by both animals.
Step 3: Add data or information
Now, add the relevant data or information to each circle. This could include specific characteristics or attributes of the sets being compared. For instance, you could list traits unique to dogs in one circle and traits unique to cats in the other circle, while the overlapping portion would include shared traits such as "four-legged" or "mammals".
Step 4: Analyze and interpret the diagram
Finally, analyze the Venn diagram to draw conclusions about the data being compared. By examining the overlapping and non-overlapping areas, you can identify similarities and differences between the sets. This analysis can provide insights into the relationship between the sets and help in making informed decisions or observations based on the data displayed.
In conclusion, following these four steps will allow you to effectively use a Venn diagram to compare and analyze different sets of data. Whether you are comparing characteristics, attributes, or any other form of data, Venn diagrams serve as a valuable visual representation tool.
What are the steps of Venn diagram?
Venn diagrams are a useful tool for organizing and visualizing data, especially when comparing different sets of information. They are named after the English mathematician John Venn, who introduced them in the late 19th century.
The steps to create a Venn diagram are relatively simple, and they can be done using HTML or any other graphic software. Here are the main steps:
Step 1: Determine the sets to be represented in the Venn diagram. These sets can be anything you want to compare, such as animals, colors, or types of food. For example, let's say we want to compare the sets of fruits, vegetables, and dairy products.
Step 2: Draw overlapping circles or ellipses on your HTML canvas. Each circle or ellipse represents a set. In this case, we will draw three overlapping circles representing fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. Make sure that the circles or ellipses overlap in some regions to visually represent the shared elements between the sets.
Step 3: Label each circle or ellipse with the name of the set it represents. For example, label one circle as "Fruits," another as "Vegetables," and the remaining one as "Dairy Products."
Step 4: Fill in the overlapping regions with the elements that are shared between sets. For example, if apples and oranges are both fruits and can be classified as dairy products, they would be placed in the overlapping region of the "Fruits" and "Dairy Products" circles. Similarly, if carrots are both vegetables and fruits, they would be placed in the overlapping region of the "Vegetables" and "Fruits" circles.
Step 5: Finally, label the non-overlapping regions with the elements that belong exclusively to each set. For example, label the area outside all circles or ellipses as "Neither fruits nor vegetables nor dairy products," since it represents items that do not belong to any of the sets being compared.
In summary, creating a Venn diagram involves determining the sets to be compared, drawing overlapping circles or ellipses to represent the sets, labeling each circle or ellipse, filling in the overlapping regions, and labeling the non-overlapping regions. This visual representation helps to analyze and understand the relationships between different sets of information.
What is a 4 way Venn diagram?
A 4-way Venn diagram is a graphical representation used to display the relationships between four sets of data. It is an extension of the more commonly known Venn diagram, which typically represents the relationships between two or three sets.
The diagram consists of four overlapping circles, each representing a different set. The overlap between the circles shows the intersection or common elements between the sets. In a 4-way Venn diagram, the number of intersections increases, allowing for a more detailed analysis of the relationships between the sets.
4-way Venn diagrams are often used in fields such as mathematics, statistics, and data analysis to compare and contrast different attributes or categories within a dataset. They can be especially useful when dealing with complex datasets that involve multiple variables or characteristics.
One example of how a 4-way Venn diagram can be used is in analyzing the preferences of customers in a retail store. The four sets could represent different product categories such as electronics, clothing, beauty, and home goods. The intersections between the circles would show which categories have overlapping customer preferences, providing insights into cross-selling opportunities or potential areas for product diversification.
Creating a 4-way Venn diagram can be done manually using a compass and ruler, or by utilizing specialized software or online tools. The circles are typically labeled with the names or categories of the sets being compared, and the intersections are labeled with the corresponding attributes or characteristics.
It is important to note that a 4-way Venn diagram may not always be applicable or necessary, depending on the nature of the data being analyzed. In some cases, a simpler Venn diagram or other visualization technique may suffice for representing the relationships between sets.
In conclusion, a 4-way Venn diagram is a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing the relationships between four sets of data. It can provide a deeper understanding of the interactions and commonalities between different categories or attributes. Using this type of diagram correctly can enhance decision-making processes and facilitate data-driven insights.
How do you represent 4 sets in a Venn diagram?
Representing 4 sets in a Venn diagram requires a slightly different approach compared to the traditional 3-set Venn diagram. In a Venn diagram, circles are used to represent sets, with each circle representing a separate set. The overlapping regions show elements that are common to two or more sets.
For a 4-set Venn diagram, four circles are used to represent the four sets. These circles can overlap in various ways to represent the relationships between the sets.
The first step in creating a 4-set Venn diagram is to identify the four sets and determine their relationships. For example, let's say we have sets A, B, C, and D.
The second step is to determine the overlapping regions. For a 4-set Venn diagram, there are a total of 15 possible regions. However, not all regions need to be included. We can choose to include only the regions that are relevant to the sets being represented.
The third step is to assign elements to the appropriate regions. Each element should be placed in the corresponding region based on its membership in the sets being represented. If an element belongs to multiple sets, it should be placed in the overlapping region(s) that represent the intersection of those sets.
Finally, the 4-set Venn diagram should be labeled to clearly indicate the sets being represented and the elements included in each region. This labeling helps viewers understand the diagram and the relationships between the sets.
In conclusion, representing 4 sets in a Venn diagram involves identifying the sets, determining the overlapping regions, assigning elements to the appropriate regions, and labeling the diagram. This visual representation helps us understand the relationships between different sets and the elements they have in common.
How to use a Venn diagram?
A Venn diagram is a graphical representation that depicts the logical relationships between different sets of data. It consists of overlapping circles or ellipses, with each circle representing a set and the overlapping region representing the intersection of the sets.
To use a Venn diagram effectively, follow these steps:
- Identify the sets: Determine the different sets or categories you want to compare or analyze. For example, if you are analyzing the characteristics of cats and dogs, you would have two sets: cats and dogs.
- Create a Venn diagram: Draw two or more circles that represent the sets you identified. Make sure the circles overlap to indicate the areas of intersection.
- Label the sets: Label each circle with the name of the set it represents. In our example, label one circle as "Cats" and the other as "Dogs".
- Add elements: Determine the elements or attributes that belong to each set and place them within the respective circles. For example, if you want to compare the characteristics of cats and dogs, you would write the specific attributes inside each circle.
- Identify overlaps: Identify the shared elements between the sets by writing them in the overlapping region. These elements represent the characteristics or attributes that are common to both sets.
- Analyze the diagram: Interpret the Venn diagram to understand the relationships and comparisons between the sets. You can analyze the size of the overlapping regions to determine the degree of overlap between sets and identify unique characteristics of each set.
Using a Venn diagram can help to visualize the relationships between different sets and facilitate the comparison and analysis of data. It provides a clear and concise way to represent complex information, making it a valuable tool in various fields such as mathematics, statistics, and problem-solving.
